Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are essential components of modern buildings, ensuring comfort and maintaining optimal indoor environments. One crucial aspect of HVAC systems is their ability to provide both heating and cooling functions, offering year-round climate control.
Which HVAC systems can provide both heating and cooling? Let’s explore the different HVAC systems that can seamlessly switch between heating and cooling modes, exploring their features, advantages, and considerations for choosing the right system for your home from the pros at ASI Heating & Air.
What Are HVAC Systems?
Though they can vary between systems, the components of an HVAC system may include:
- Heating equipment:HVAC systems have either a furnace or a heat pump to generate or move heat.
- Cooling equipment:HVAC systems have cooling equipment like an air conditioner or heat pump to provide cooling.
- Ventilation system:HVAC systems have ventilation using vents or registers, air ducts, exhaust fans, or fresh air intake.
- Thermostat:The thermostat controls the temperature by regulating the operation of the heating or cooling equipment.
- Humidity control:HVAC systems often have a humidifier or a dehumidifier component to adjust the humidity in the air.
- Air filters:HVAC systems have air filters to remove particles and contaminants from air to improve indoor air quality.
- Controls and sensors:HVAC systems have thermostats, sensors, and other devices to monitor and regulate the system.
- Refrigerant:Refrigerant is used in cooling systems to absorb and release heat.
- Condensate drain:The condensate drain removes condensation produced during the cooling process.
- Compressor:In the refrigeration cycle, the compressor compresses the refrigerant gas to increase its temperature and pressure.
- Evaporator coil:The evaporator coil absorbs heat from the air and is part of the indoor unit of the cooling system.
- Condenser coil:The condenser coil releases heat to the outside air and is part of the outdoor unit of the cooling system.
These components work together to maintain a comfortable indoor environment by controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality. The specific configuration and components can vary based on the type of HVAC system.
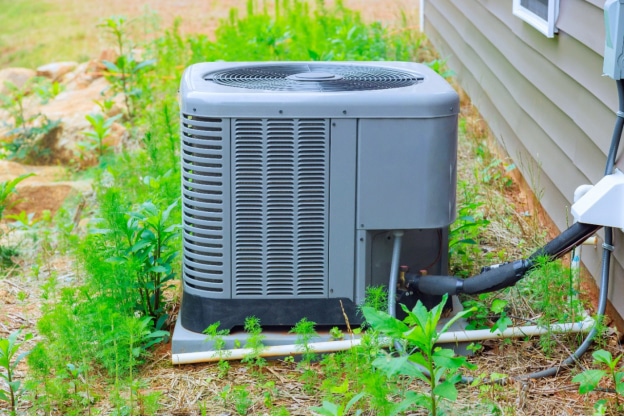

How Does an HVAC System Work?
HVAC systems regulate temperature and maintain air quality through proper ventilation. They all have a heating system, cooling system, and ventilation system. With a furnace, the heat is generated through electricity or the burning of a fuel, such as natural gas or propane. With a heat pump, the heat is absorbed from outside and distributed inside.
For cooling, the air conditioning absorbs the heat from inside and moves it to the outdoor unit, where the warm refrigerant gas is moved to the compressor to remove ambient heat and turn it into its liquid form. This liquid refrigerant is then passed through a condenser and evaporator coil, which converts the liquid refrigerant into cool air that is passed through the vents and air ducts.
HVAC Systems That Offer Both Heating and Cooling
Heat Pumps
The advantages of heat pumps include:
- Energy efficiency:Heat pumps have the main advantage of energy efficiency as they move heat instead of generating it.
- Year-round comfort:Heat pumps can operate in both heating and cooling modes, ensuring comfort throughout the year.
- Environmentally friendly:Because they use ambient heat, heat pumps reduce reliance on traditional heating methods, minimizing environmental impact.
The considerations for heat pumps include:
- Performance in extreme temperatures:Heat pump efficiency may decrease in extremely cold climates, requiring supplementary heating sources.
- Installation costs:Initial installation costs can be higher than traditional systems, but long-term savings may offset the price.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
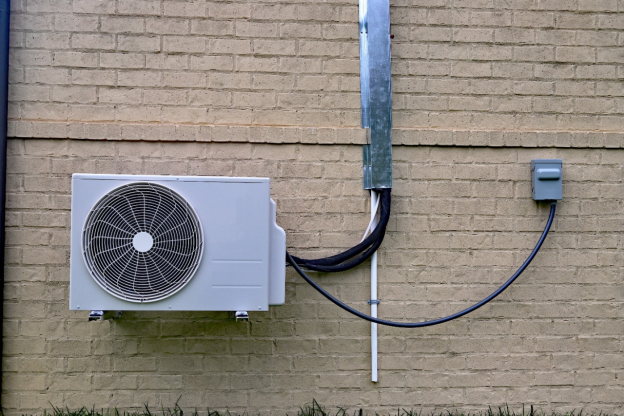
Ductless mini-split systems consist of an outdoor condenser unit and one or more indoor air handlers, connected by refrigerant lines. These systems are flexible, allowing for independent temperature control in different zones. Mini-split systems can provide both heating and cooling by reversing the refrigeration cycle, much like heat pumps.
The advantages of mini-split systems include:
- Zoning capability:Mini splits enable customized temperature control in individual rooms or zones, optimizing energy usage.
- Ductless design:The absence of ductwork reduces energy losses and allows for easier installation in existing buildings.
- Energy efficiency:Like heat pumps, mini splits can be highly energy efficient, contributing to lower utility bills.
The considerations for a mini-split system include:
- Upfront costs:Initial costs can be higher than traditional systems, particularly when installing multiple indoor units.
- Aesthetics:The presence of the indoor units on walls or ceilings may not suit every architectural or design preference.
Hybrid HVAC Systems

Hybrid HVAC systems combine the strengths of a traditional furnace and a heat pump, providing both heating and cooling options. These systems automatically switch between the two modes based on outdoor conditions and energy efficiency considerations.
The advantages of a hybrid system include:
- Energy efficiency:Hybrid systems optimize energy usage by selecting the most efficient mode depending on external temperatures.
- Reliable heating in cold climates:In extremely cold weather, the furnace component ensures reliable heating performance.
- Environmental impact:By utilizing a heat pump, hybrid systems contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The considerations for a hybrid HVAC system include:
- Initial costs:Hybrid systems may have higher upfront costs due to the integration of both heating technologies.
- Maintenance:Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance of both the heat pump and furnace components.
Considerations for Choosing an HVAC System
When you’re selecting an HVAC system that provides both heating and cooling, several factors should be considered to ensure the chosen system meets specific requirements and preferences.
Climate Considerations

The climate of the region where the HVAC system will be installed plays a crucial role in areas with moderate climates, heat pumps, or ductless mini-split systems may be sufficient. In colder climates, a hybrid system or a backup heating source may be necessary for reliable heating during winter.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key consideration for both environmental sustainability and cost savings. Look for systems with high seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) and heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF) ratings. These ratings indicate the efficiency of the system in cooling and heating modes, respectively.
Installation and Space Requirements
Consider the available space for installing HVAC equipment and whether ductwork is feasible. Ductless mini-split systems are advantageous in spaces where traditional ductwork is impractical, offering flexibility in installation.
Budget Considerations
Evaluate both upfronts costs and long-term operating costs when determining the budget for an HVAC system. While more energy-efficient systems may have higher initial costs, the potential for lower utility bills over time should be factored into the decision-making process.
System Controls and Smart Features
Modern HVAC systems often come with advanced controls and smart features that enhance user convenience and energy management. Consider systems with programmable thermostats, remote access, and compatibility with smart home automation platforms for optimal control and efficiency.
The Importance of HVAC Maintenance
Regardless of the HVAC system you choose, regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance not only ensures that the system operates efficiently but also helps prevent potential breakdowns and costly repairs.
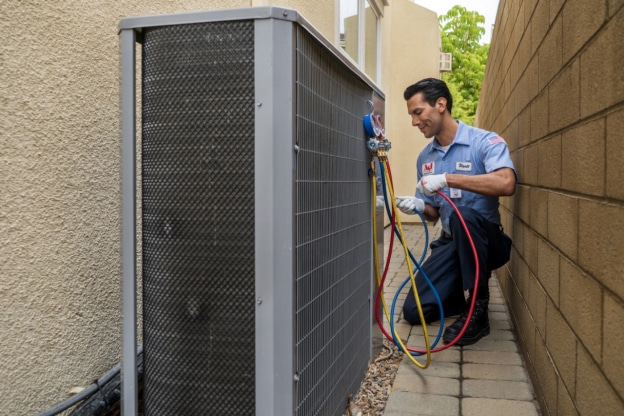

Some important maintenance practices include:
- Filter replacement:Regularly replace your air filters to maintain good indoor air quality and prevent the HVAC system from working harder than necessary. Clogged filters can lead to reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption.
- Professional inspections:Schedule annual professional inspections to identify and address any issues promptly. Professionals can check refrigerant levels, inspect components for wear and tear, and ensure that the system operates at peak efficiency.
- Programmable thermostats and smart controls:Use programmable thermostats and smart controls to create temperature schedules based on occupancy patterns. This helps optimize energy usage by adjusting temperatures during periods of lower activity.
- Sealing ductwork:If the HVAC system has ductwork, it’s important that the ductwork is properly sealed to prevent air leaks. Leaky ducts can lead to energy losses and reduced efficiency.
Upgrade Your HVAC System
If you’re looking for an HVAC system for heating and cooling, there are plenty of options to choose from, from heat pumps to ductless mini splits to traditional furnaces and air conditioning. It’s important to consider all your options and the factors that affect the system you choose, including energy efficiency, comfort, and long-term costs. In addition, you have to invest in professional HVAC maintenance to keep your system running its best for its entire lifespan.
If you’re considering an HVAC upgrade for your home, contact the pros at ASI Heating & Air to schedule your appointment.







